Difference between revisions of "Ghost nodes"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
where $\Omega = B(\boldsymbol{0}, 1) - B(\boldsymbol{1}, 1.5)$, $\partial \Omega_{+}$ is the part of the boundary with the nonnegative $x$ coordinate and $\partial \Omega_{-}$ the part of the boundary with negative $x$ coordinate. | where $\Omega = B(\boldsymbol{0}, 1) - B(\boldsymbol{1}, 1.5)$, $\partial \Omega_{+}$ is the part of the boundary with the nonnegative $x$ coordinate and $\partial \Omega_{-}$ the part of the boundary with negative $x$ coordinate. | ||
| + | The code below constructs ghost nodes and remembers the corresponding ghost node for each boundary node. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | ||
| − | int | + | Range<int> gh(domain.size(), -1); // Maps boundary nodes to their corresponding ghost nodes. |
| + | for (int i : neu) { // Add ghost nodes for each Neumann boundary node | ||
| + | gh[i] = domain.addInternalNode(domain.pos(i) + dx*domain.normal(i), 2); | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | When assembling the system, | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | ||
| + | for (int i : interior) { | ||
| + | op.lap(i) = 1.0; // Equation | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | for (int i : dir) { | ||
| + | op.value(i) = 0.0; // Dirichlet | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | for (int i : neu) { | ||
| + | op.neumann(i, domain.normal(i)) = 0.0; // Neumann | ||
| + | // Equation holds also on the boundary, write it in the row corresponding to the ghost node. | ||
| + | op.lap(i, gh[i]) = 1.0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 09:58, 18 May 2019
Go back to Examples.
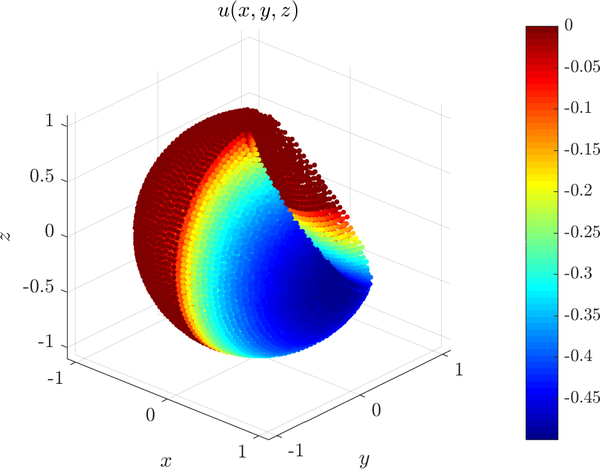
See the Ghost nodes (theory) page for what ghost nodes and how they are used. We will use them in this example to reliably solver a 3D mixed Dirichlet and Neumann problem on an irregular domain.
We will solve the problem
$\nabla^2 u = 1 \text{ in } \Omega, \quad \frac{\partial u}{\partial n} = 0 \text{ on } \partial \Omega_{+}, \quad u = 0 \text{ on } \partial \Omega_{-}$
where $\Omega = B(\boldsymbol{0}, 1) - B(\boldsymbol{1}, 1.5)$, $\partial \Omega_{+}$ is the part of the boundary with the nonnegative $x$ coordinate and $\partial \Omega_{-}$ the part of the boundary with negative $x$ coordinate.
The code below constructs ghost nodes and remembers the corresponding ghost node for each boundary node.
Range<int> gh(domain.size(), -1); // Maps boundary nodes to their corresponding ghost nodes.
for (int i : neu) { // Add ghost nodes for each Neumann boundary node
gh[i] = domain.addInternalNode(domain.pos(i) + dx*domain.normal(i), 2);
}
When assembling the system,
for (int i : interior) {
op.lap(i) = 1.0; // Equation
}
for (int i : dir) {
op.value(i) = 0.0; // Dirichlet
}
for (int i : neu) {
op.neumann(i, domain.normal(i)) = 0.0; // Neumann
// Equation holds also on the boundary, write it in the row corresponding to the ghost node.
op.lap(i, gh[i]) = 1.0;
}
The solution is shown below:
Go back to Examples.