Difference between revisions of "Natural convection in 3D irregular domain"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:DVD_3D.png|400px]] | [[File:DVD_3D.png|400px]] | ||
[[File:DVD_3D_irreg.png|400px]] | [[File:DVD_3D_irreg.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! style="text-align: center;" | Ra | ||
| + | ! $v_{max}$ | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! $x$ | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! $u_{max}$ | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! $y$ | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | present | ||
| + | | ref a | ||
| + | | ref b | ||
| + | | present | ||
| + | | ref a | ||
| + | | ref b | ||
| + | | present | ||
| + | | ref a | ||
| + | | ref b | ||
| + | | present | ||
| + | | ref a | ||
| + | | ref b | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2D | ||
| + | | $10^6$ | ||
| + | | 0.2628 | ||
| + | | 0.2604 | ||
| + | | 0.2627 | ||
| + | | 0.0378 | ||
| + | | 0.0380 | ||
| + | | 0.0390 | ||
| + | | 0.0781 | ||
| + | | 0.0765 | ||
| + | | 0.0782 | ||
| + | | 0.8476 | ||
| + | | 0.8510 | ||
| + | | 0.0390 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | $10^7$ | ||
| + | | 0.2633 | ||
| + | | 0.2580 | ||
| + | | 0.2579 | ||
| + | | 0.0226 | ||
| + | | 0.0230 | ||
| + | | 0.0210 | ||
| + | | 0.0588 | ||
| + | | 0.0547 | ||
| + | | 0.0561 | ||
| + | | 0.8705 | ||
| + | | 0.8880 | ||
| + | | 0.0210 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | $10^8$ | ||
| + | | 0.2557 | ||
| + | | 0.2587 | ||
| + | | 0.2487 | ||
| + | | 0.0149 | ||
| + | | 0.0110 | ||
| + | | 0.0090 | ||
| + | | 0.0314 | ||
| + | | 0.0379 | ||
| + | | 0.0331 | ||
| + | | 0.9189 | ||
| + | | 0.9430 | ||
| + | | 0.0090 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3D | ||
| + | | $10^4$ | ||
| + | | 0.2495 | ||
| + | | 0.2218 | ||
| + | | 0.2252 | ||
| + | | 0.8500 | ||
| + | | 0.8873 | ||
| + | | 0.8833 | ||
| + | | 0.2435 | ||
| + | | 0.1968 | ||
| + | | 0.2013 | ||
| + | | 0.1611 | ||
| + | | 0.1799 | ||
| + | | 0.1833 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | $10^5$ | ||
| + | | 0.2545 | ||
| + | | 0.2442 | ||
| + | | 0.2471 | ||
| + | | 0.9402 | ||
| + | | 0.9317 | ||
| + | | 0.9353 | ||
| + | | 0.1564 | ||
| + | | 0.1426 | ||
| + | | 0.1468 | ||
| + | | 0.1447 | ||
| + | | 0.1493 | ||
| + | | 0.1453 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | $10^6$ | ||
| + | | 0.2564 | ||
| + | | 0.2556 | ||
| + | | 0.2588 | ||
| + | | 0.9614 | ||
| + | | 0.9653 | ||
| + | | 0.9669 | ||
| + | | 0.0841 | ||
| + | | 0.0816 | ||
| + | | 0.0841 | ||
| + | | 0.1435 | ||
| + | | 0.1403 | ||
| + | | 0.1443 | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 18 May 2019
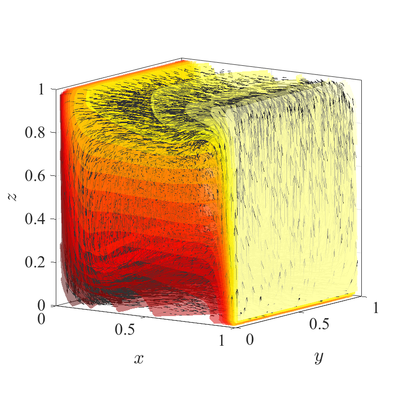
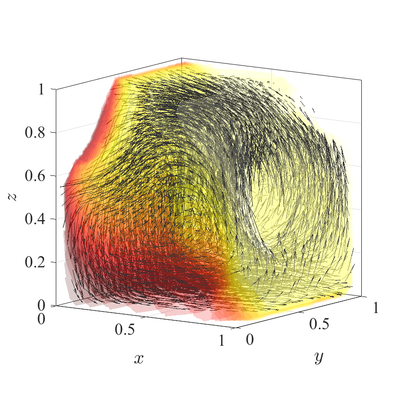
The classical De Vahl Davis natural convection test can be extended to 3D. In below figures steady state temperature contour and velocity quiver plots for Ra$=10^6$ case in 3D are presented. A more quantitative analysis is done by comparing characteristic values, i.e.\ peak positions and values of cross section velocities, with data available in literature~\cite{fusegi1991numerical}. We analyze six different cases, namely $\textup{Ra} = 10^6,10^7,10^8$ in 2D, and $\textup{Ra} = 10^4,10^5,10^6$ in 3D. The comparison in presented in~\cref{tab:ff-data}.
All spatial operators are discretized using RBF-FD with $r^3$ PHS radial basis functions, augmented with monomials up to order $2$, with the closest $25$ nodes used as a stencil. For the time discretization time step $\Delta t=10^{-3}$ was used for all cases. Nodal distance $h=0.01$ is used for simulations in 2D and $h=0.25$ for simulations in 3D. Boundaries with Neumann boundary conditions are additionally treated with ghost nodes Ghost nodes (theory).
| Ra | $v_{max}$ | $x$ | $u_{max}$ | $y$ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| present | ref a | ref b | present | ref a | ref b | present | ref a | ref b | present | ref a | ref b | ||
| 2D | $10^6$ | 0.2628 | 0.2604 | 0.2627 | 0.0378 | 0.0380 | 0.0390 | 0.0781 | 0.0765 | 0.0782 | 0.8476 | 0.8510 | 0.0390 |
| $10^7$ | 0.2633 | 0.2580 | 0.2579 | 0.0226 | 0.0230 | 0.0210 | 0.0588 | 0.0547 | 0.0561 | 0.8705 | 0.8880 | 0.0210 | |
| $10^8$ | 0.2557 | 0.2587 | 0.2487 | 0.0149 | 0.0110 | 0.0090 | 0.0314 | 0.0379 | 0.0331 | 0.9189 | 0.9430 | 0.0090 | |
| 3D | $10^4$ | 0.2495 | 0.2218 | 0.2252 | 0.8500 | 0.8873 | 0.8833 | 0.2435 | 0.1968 | 0.2013 | 0.1611 | 0.1799 | 0.1833 |
| $10^5$ | 0.2545 | 0.2442 | 0.2471 | 0.9402 | 0.9317 | 0.9353 | 0.1564 | 0.1426 | 0.1468 | 0.1447 | 0.1493 | 0.1453 | |
| $10^6$ | 0.2564 | 0.2556 | 0.2588 | 0.9614 | 0.9653 | 0.9669 | 0.0841 | 0.0816 | 0.0841 | 0.1435 | 0.1403 | 0.1443 |