Electromagnetic scattering
Go back to Examples.
In this example we will show how to solve an electromagnetic scattering problem in Medusa. The example uses both complex numbers as well as domain coupling, so we recommend firstly reading tutorials on Coupled domains and Complex-valued problems.
Anisotropic cylinder
Let us first quickly derive the problem we are about to solve. Beginning with the electromagnetic wave equation in anisotropic media
\[ \label{eq:frekaniwave} \nabla \times \left( \underline{\varepsilon}^{-1} \nabla \times \boldsymbol{H} \right) = \omega^2 \mu_0 \varepsilon_0 \underline{\mu} \boldsymbol{H}, \] where \(\underline{\varepsilon}\) is the relative dielectric tensor, and \(\underline{\mu}\) is the magnetic permeability tensor of the anisotropic material
\[ \label{eq:relepsmi} \underline{\varepsilon} = \begin{pmatrix} \varepsilon_{xx} & \varepsilon_{xy} & \varepsilon_{xz} \\ \varepsilon_{yx} & \varepsilon_{yy} & \varepsilon_{yz} \\ \varepsilon_{zx} & \varepsilon_{zy} & \varepsilon_{zz} \end{pmatrix} , \qquad \underline{\mu} = \begin{pmatrix} \mu_{xx} & \mu_{xy} & \mu_{xz} \\ \mu_{yx} & \mu_{yy} & \mu_{yz} \\ \mu_{zx} & \mu_{zy} & \mu_{zz} \end{pmatrix}. \]
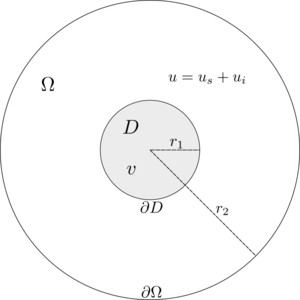
Let $D \subset \R^2$ be the cross section of an infinitely long anisotropic dielectric cylindrical scatterer with its axis alligned with the $z$-axis, surrounded by a free space, with an outward normal $n$ on boundary $\partial D$. The cylinder is isotropic along its axis, and is excited by an $e^{i \omega t}$ time-harmonic plane wave with $\b{TM}^z$ polarization, with $\omega$ standing for its angular frequency. Let $v \in C^2(\C)$ denote the complex valued field inside the scatterer and $u \in C^2(\C)$ the field outside of the scatterer. Field $u$ can be further decomposed into the incident $u^i$ and the scattered field $u^s$.
The fields $u^s$ and $v$ must satisfy the set of PDE \begin{align*} \nabla \cdot A \nabla v + \epsilon_r k^2 \thinspace v = 0 \qquad &\text{in} \quad D \label{eq:inner} \\ \nabla^2 u^s + k^2 \thinspace u^s = 0 \qquad &\text{in} \quad \Omega \setminus D \label{eq:outer} \end{align*} with boundary conditions \begin{align*} v - u^s =u^i \qquad &\text{on} \quad \partial D \label{eq:BC1} \\ \frac{\partial v}{\partial n_A\!\!\!} - \frac{\partial u^s}{\partial n} = \frac{\partial u^i}{\partial n} \qquad &\text{on} \quad \partial D \label{eq:BC2} \\ \frac{\partial u^s}{\partial n} + \left( ik + \frac{1}{2r_2} \right)u^s = 0 \quad &\text{on} \quad \partial \Omega \end{align*} where $k = \omega \sqrt{\mu_0 \epsilon_0} = \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda}$ is the wave number of free space, $\mu_0$ and $\epsilon_0$ are magnetic permeability and electric permittivity of free space, while $\epsilon_r$ is the relative electric permittivity of the scatterer. Relative magnetic permeability matrix $A$ is of the following form \begin{equation*} A = \frac{1}{\mu_{xx}\mu_{yy} - \mu_{xy}^2} \begin{pmatrix} \mu_{xx} & \mu_{xy} \\ \mu_{xy} & \mu_{yy} \end{pmatrix} \end{equation*} and the anisotropic normal derivative is calculated as \begin{equation*} \frac{\partial v}{\partial n_A\!\!\!} = n \cdot A \nabla {v}. \end{equation*}
The system is implemented below
1 for (int i : inner.interior()) {
2 //Eq on the inner circle
3 mxx * op_inner.der2(i, 0, 0) + myy * op_inner.der2(i, 1, 1) +
4 (mxy + myx) * op_inner.der2(i, 0, 1)
5 + k0 * k0 * er * op_inner.value(i) = 0;
6 }
7 for (int i : inner.boundary()) {
8 //dirichlet, u_inside - u_scattered = u_incident <- incoming wave from t0 angle
9 double x = inner.pos(i, 0);
10 double y = inner.pos(i, 1);
11 double theta = atan2(y, x); // get phase
12
13 // in the upper side of the matrix
14 std::complex<double> incident = std::exp(1.0i * k0 * (x * std::cos(t0) + y * std::sin(t0)));
15 op_inner.value(i) + (-1) * op_outer.value(inner_bnd[i], N_outer + i) = incident;
16
17 // Neumann boundary condition on the inside circle
18 auto norm = inner.normal(i);
19 double n0 = norm[0];
20 double n1 = norm[1];
21
22 // Anisotropic normal derivative
23 // (n0*mxx+n1*myx)*v_x + (n0*mxy+n1*myy)*v_y + du/dn = d(incident)/dn
24 op_outer.neumann(inner_bnd[i], outer.normal(inner_bnd[i]))
25 + (n0 * mxx + n1 * myx) * op_inner.der1(i, 0, -N_outer + inner_bnd[i])
26 + (n0 * mxy + n1 * myy) * op_inner.der1(i, 1, -N_outer + inner_bnd[i])
27 = 1.0i * k0 * std::cos(theta - t0) *
28 std::exp(1.0i * k0 * (x * std::cos(t0) + y * std::sin(t0)));
29 }
30 for (int i : outer.interior()) {
31 // wave equation for the outer region
32 op_outer.lap(i) + k0 * k0 * op_outer.value(i) = 0;
33 }
34 for (int i : outer_bnd) {
35 // Sommerfeld boundary condition
36 op_outer.neumann(i, outer.normal(i)) + (k0 * 1.0i + 1 / (2 * r2)) * op_outer.value(i) = 0.0;
37 }
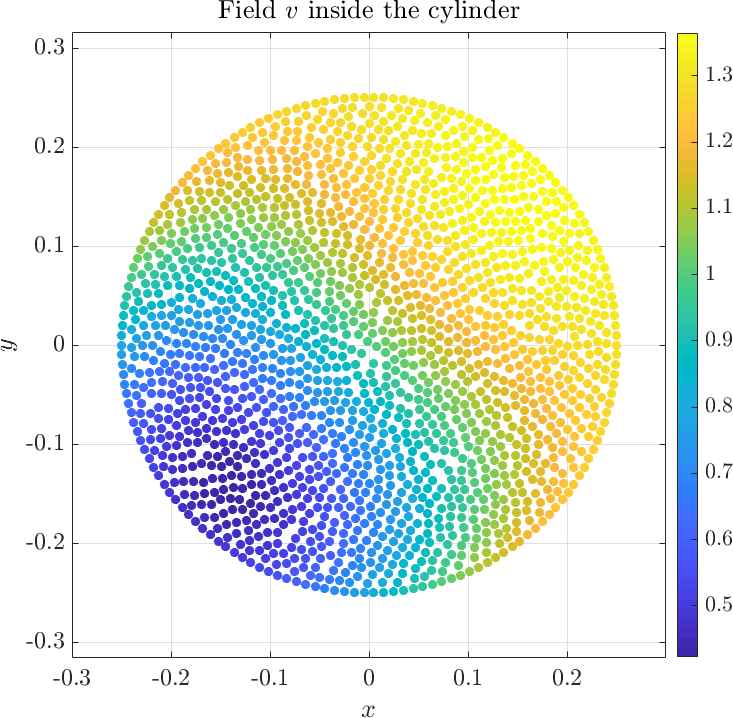
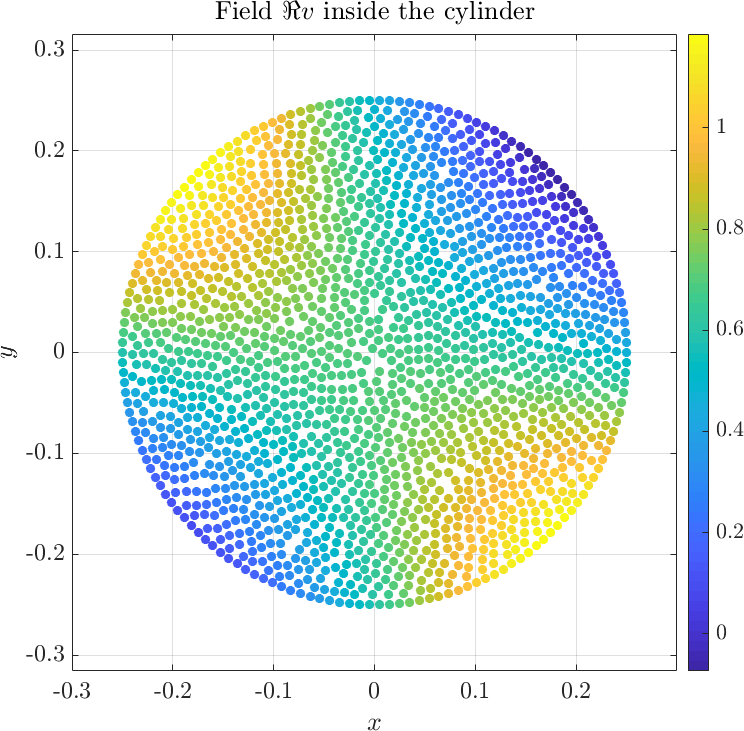
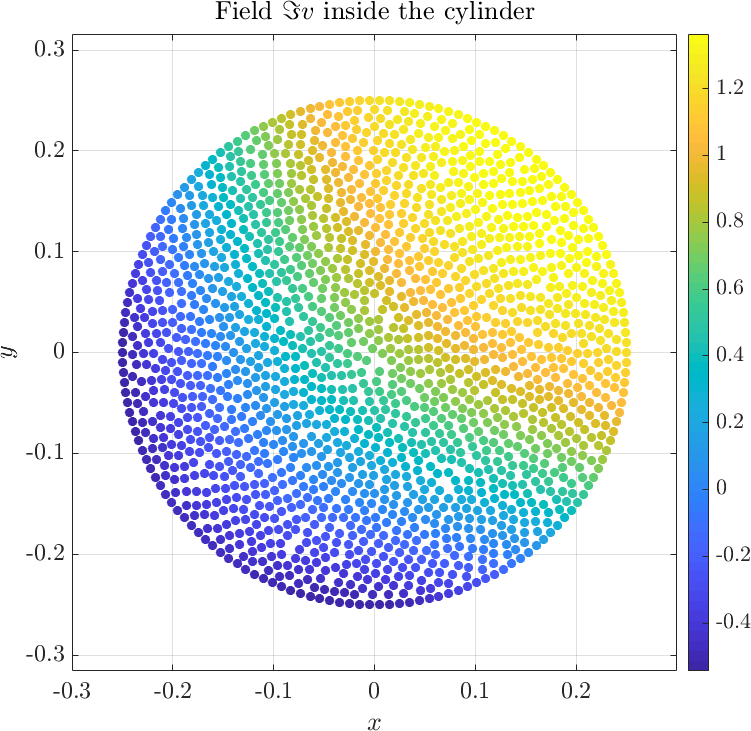
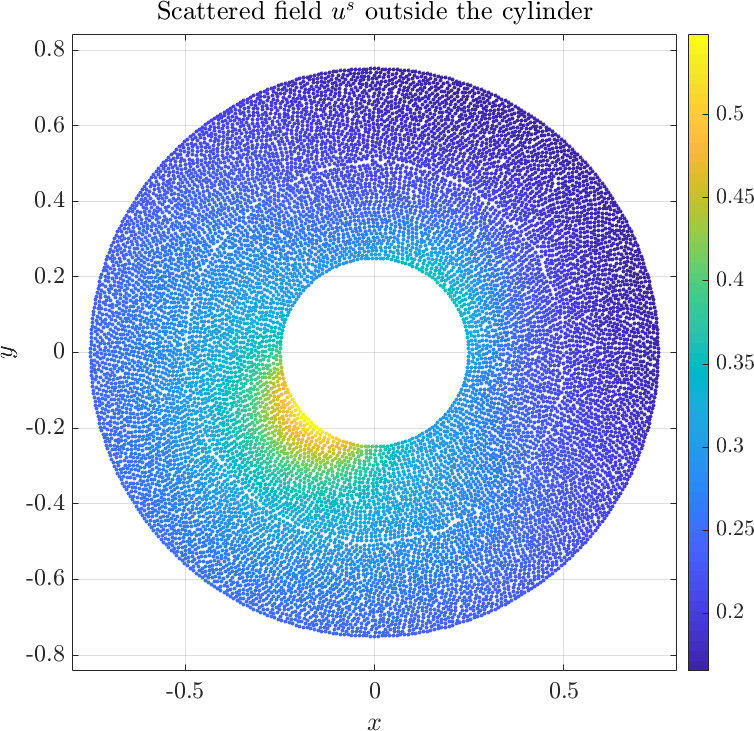
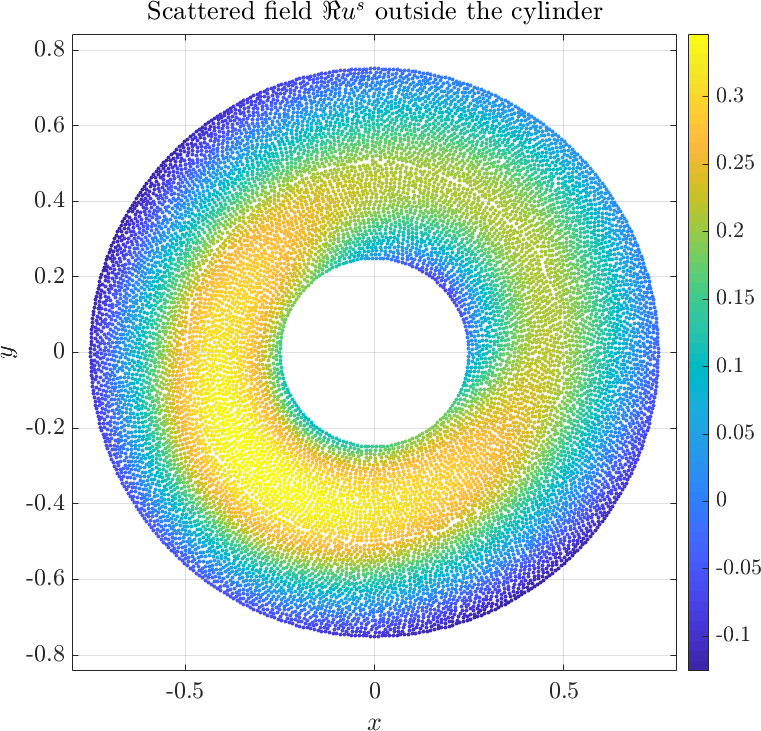
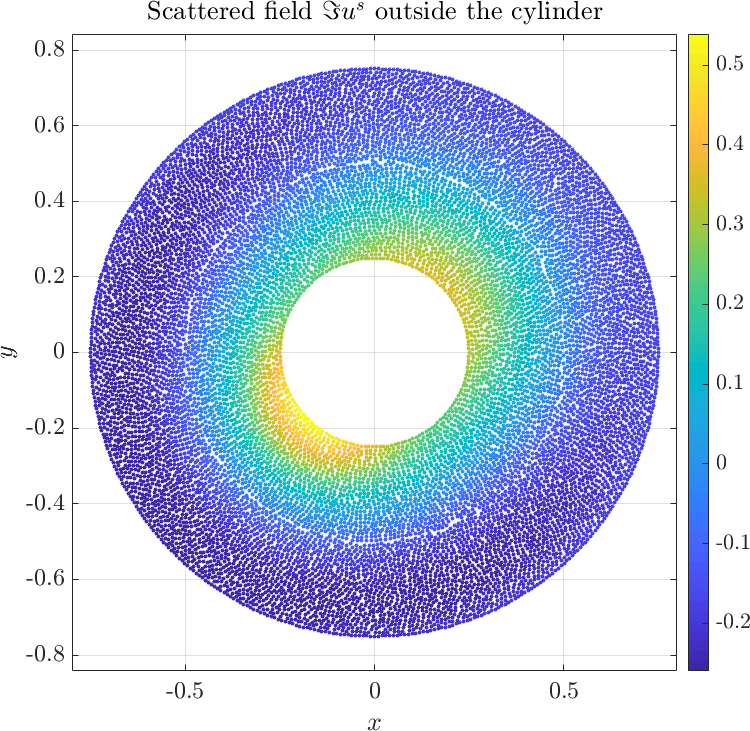
Solving the system gives the complex valued solution to both fields. The solution is plotted below.
The example can be found here anisotropic_cylinder.cpp, and the matlab plot script can be found here anisotropic_cylinder.m. A more comprehensive description of thre problem can be found in the paper [1].
References
- ↑ Stojanovič, B., & Slak, J., & Kosec, G. (2019). RBF-FD Solution of Electromagnetic Scattering Problem. MIPRO 2019 : 42nd International Convention, May 20 -24, 2019, Opatija, Croatia : proceedings.
Go back to Examples.