Fretting fatigue case
Click on Solid Mechanics to go back.
Contents
Introdution
This case is an extension of the classical Hertzian contact, as defined in Pereira et al. (2016) [1] and described in detail in Hojjati-Talemi et al. (2014) [2]
Description of the case and parameters
MLSM numerical solution for bulk load
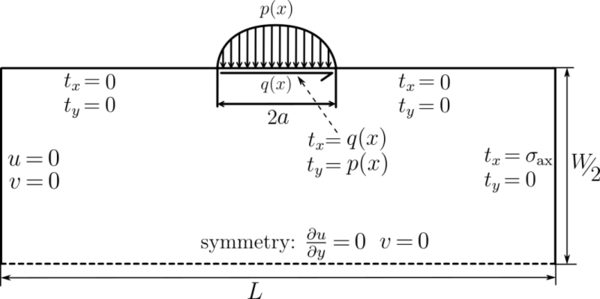
Case definition
We are solving the equation $$(\lambda + \mu) \nabla (\nabla \cdot \b{u}) + \mu \nabla^2 \b{u} = 0$$ on the domain $D = [-L/2, L/2] \times [-H/2, 0]$. Componentwise $\b{u} = [u; v]$. The boundary conditions are:
- top: $\vec{t}(x) = (q(x), -p(x))$ or componentwise $\mu \frac{\partial u}{\partial y}(x, 0) + \mu \frac{\partial v}{\partial x}(x, 0) = q(x)$ and $(2 \mu+\lambda) \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}(x, 0) + \lambda \frac{\partial v}{\partial y}(x, 0) = -p(x)$ .
- left: $\b{u} = 0$ or componentwise $u(-L/2, y) = v(-L/2, y) = 0$.
- bottom: up-down symmetry conditions: componentwise $\frac{\partial u}{\partial y}(x, -H/2) = 0, v(x, -H/2) = 0$.
- right: this part is traction free, ie. $\vec{t}(y) = 0$ or componentwise $\mu \frac{\partial u}{\partial y}(L/2, y) + \mu \frac{\partial v}{\partial x}(L/2, y) = 0$ and $(2 \mu+\lambda) \frac{\partial v}{\partial y}(L/2, y) + \lambda \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}(L/2, y) = 0$.
Illustration of the computational domain is presented below.
Phsyical parameters
Basic parameters are:
- $E = \unit{72.1}{GPa}$, Youngs modulus
- $\nu = 0.33$, Poissons ratio
- $L = \unit{40}{mm}$, length, width of the pad
- $H = \unit{4}{mm}$, height, thickness of the pad
- $\sigma_{ax} = \unit{100}{MPa}$, axial pressure
- $F = \unit{543}{N}$, normal force
- $Q = \unit{155}{N}$, tangential force
- $R = \unit{10}{mm}$ or $\unit{50}{mm}$, raduis of curvature of the cylindrical pad
- $COF = \mu = 0.3$ or $0.85$ or $2$, coefficient of friction
Derived parameters are, for choice of $R = \unit{10}{mm}$ and $\mu = 0.3$:
- $E^\ast = \frac{E}{2(1-\nu^2)} = \unit{40.4}{GPa}$, combined Young's modulus
- $p_{max} = p_0 = \sqrt{\frac{FE^\ast}{HR \pi}} = \unit{418.10407}{MPa}$, maximal normal pressure
- $a = 2 \sqrt{\frac{FR}{HE^\ast \pi}} = \unit{0.2067}{mm}$, semi contact width, contact region is $[-a, a] \times \{0\}$
- $c = a \sqrt{1 - \frac{Q}{\mu F}} = \unit{0.04504}{mm}$, stick zone semi width
- $e = \frac{a \sigma_{ax}}{4 \mu p_{max}} = \unit{0.041197}{mm}$, eccentricity due to axial load
Numerical solution
Comparison of this solution against FEM solution published in Pereira et al. (2016) is presented below.
The data for this plot (only MLSM data) is available to download here: File:fwo_cases_data.csv.
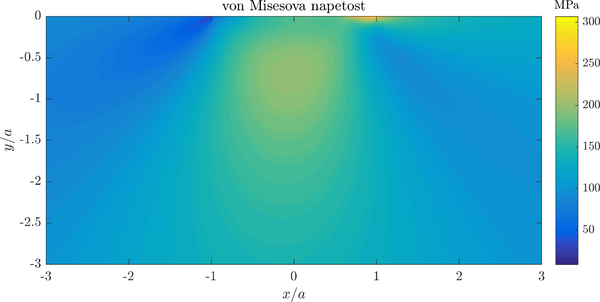
A contour plot of von Mises stress in the specimen is presented below.
Note that contour of stress are similar to the ones in Hertzian contact above, but a significant concentracion of stresses under the contact area is present.- ↑ K. Pereira et al., On the convergence of stresses in fretting fatigue, Materials 9(8) (2016), doi:10.3390/ma9080639.
- ↑ R. Hojjati-Talemi, M. A. Wahab in dr., Prediction of fretting fatigue crack initiation and propagation lifetime for cylindrical contact configuration, Tribol. Int. 76 (2014) 73–91, doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2014.02.017.